Photosynthesis Details
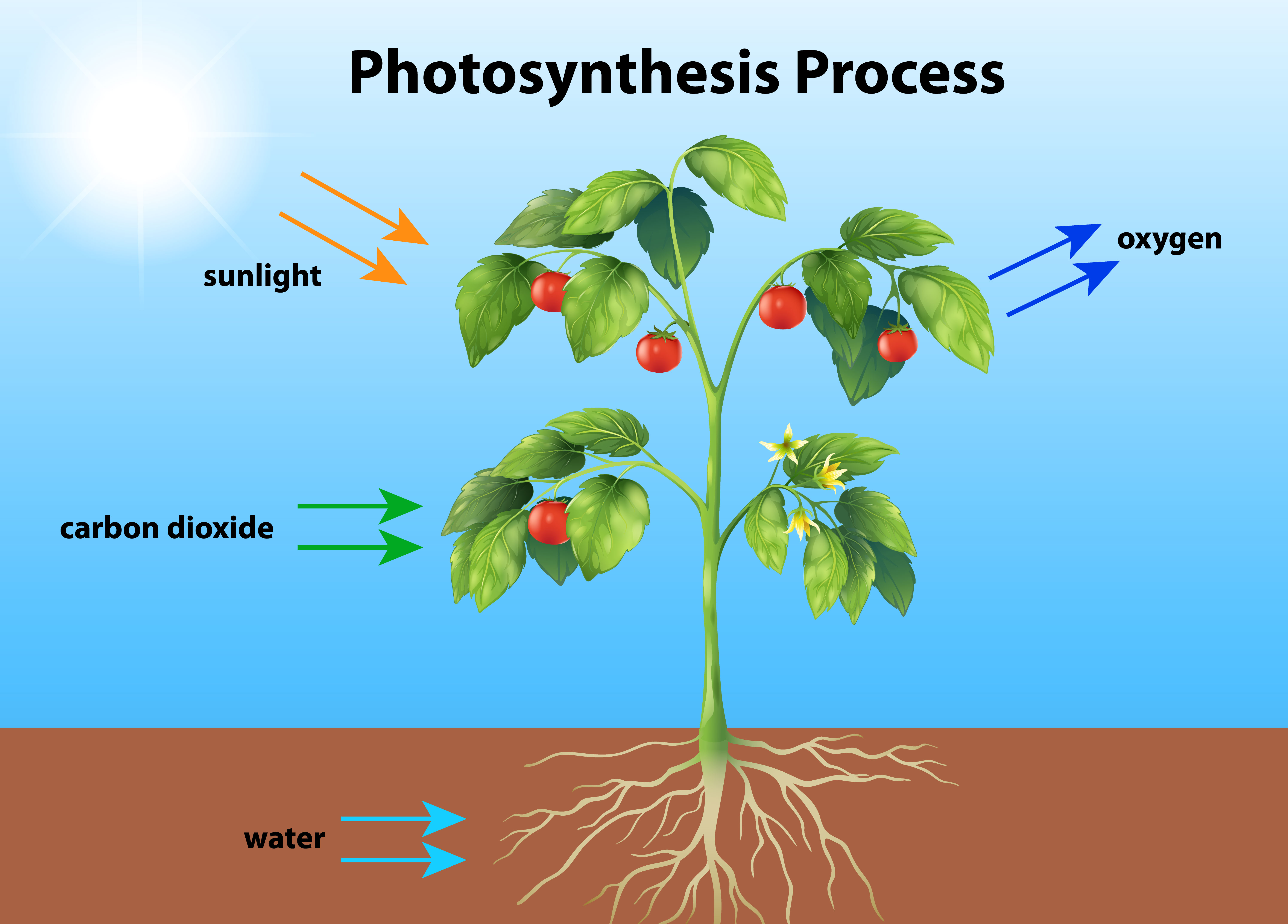
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants use sunlight to convert carbon dioxide and water into food (glucose) and oxygen.
- Plants contain special organelles called chloroplasts, which contain a pigment called chlorophyll.
- Chlorophyll absorbs light energy from the sun, primarily in the red and blue regions of the electromagnetic spectrum.
- During photosynthesis, carbon dioxide enters the plant through tiny pores called stomata, located primarily on the leaves.
- Water is absorbed by the roots of the plant and transported to the leaves.
- In the presence of sunlight, chlorophyll uses the captured energy to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose (a form of sugar) and oxygen.
- Glucose serves as the primary source of energy for the plant, fueling its growth and development.
- Oxygen, produced as a byproduct of photosynthesis, is released into the atmosphere, supporting the oxygen-dependent life forms.
- Photosynthesis is a complex process that involves several interconnected reactions, including the light-dependent and light-independent reactions.
No comments:
Post a Comment