Introduction to Microbiology
Welcome to the fascinating world of microbiology! Microbiology is the scientific study of microorganisms, which include bacteria, viruses, fungi, protozoa, and other microscopic organisms. These tiny beings play crucial roles in various aspects of life, influencing everything from human health to environmental processes.
In this overview, you'll explore several key topics within microbiology. Click on a topic to reveal more information and uncover interesting facts about each area of study.
Microbiology Topics : CLICK ON DESIRED TOPIC
- Bacteria are single-celled microorganisms that exist in various shapes and forms.
- They can be found in diverse environments, including soil, water, and the human body.
- Some bacteria are beneficial, while others can cause diseases.
- Bacteria play important roles in nutrient cycling and ecological balance.
- Bacterial classification is based on factors such as shape, staining properties, and metabolic features.
Interesting fact: There are more bacterial cells in your body than human cells.
- Viruses are infectious agents that require a host cell to multiply.
- They consist of genetic material (DNA or RNA) surrounded by a protein coat.
- Viruses can infect animals, plants, and microorganisms.
- Viral infections can cause a wide range of diseases, from the common cold to severe illnesses.
- Understanding viral structure and replication is crucial for developing antiviral treatments and vaccines.
Interesting fact: Viruses are not considered living organisms as they cannot replicate on their own.
- Fungi are eukaryotic organisms that include mushrooms, yeasts, and molds.
- They play important roles in decomposition and nutrient cycling in ecosystems.
- Some fungi form mutualistic relationships with plants, helping them absorb nutrients.
- Fungal infections can affect humans, causing diseases such as athlete's foot and candidiasis.
- Fungi have diverse forms, including single-celled yeasts and multicellular hyphae.
Interesting fact: Certain fungi are used in the production of antibiotics like penicillin.
- Protozoa are single-celled eukaryotic organisms.
- They exhibit diverse forms and locomotion methods.
- Some protozoa can cause diseases like malaria and amoebic dysentery.
- Protozoa play essential roles in aquatic ecosystems as primary consumers and decomposers.
- Understanding the life cycles of protozoa is crucial for disease prevention and control.
Interesting fact: Protozoa are responsible for diseases like malaria, which affects millions of people worldwide.
- Antibiotics are medications used to treat bacterial infections.
- They work by targeting specific bacterial structures or interfering with essential processes.
- Overuse and misuse of antibiotics can lead to the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
- Antibiotic resistance is a significant global health concern.
- Proper antibiotic stewardship is crucial to preserve the effectiveness of these medications.
Interesting fact: The discovery of penicillin by Alexander Fleming revolutionized the field of antibiotics.
- Immunology is the branch of biology that studies the immune system.
- The immune system protects the body from pathogens and foreign substances.
- It consists of various cells, tissues, and molecules that work together to defend against infections.
- Immunology research is crucial for understanding diseases and developing vaccines.
Interesting fact: Immunotherapy is a promising field that utilizes the body's immune system to fight against cancer.
- Microbes in space exploration are of great interest to astrobiologists and exobiologists.
- Research investigates the survival of microorganisms in extreme space conditions, such as radiation, vacuum, and microgravity.
- Understanding the resistance and adaptation of microbes to space environments helps assess the potential for life on other planets and the possibility of interplanetary contamination.
- Microbes can serve as model organisms to study fundamental questions related to the origin of life and the limits of habitability.
- Exploring the microbial frontier in space provides insights into the potential for extraterrestrial life and our place in the universe.
Interesting fact: Microbes have survived exposure to the harsh conditions of outer space during experiments conducted on the International Space Station.
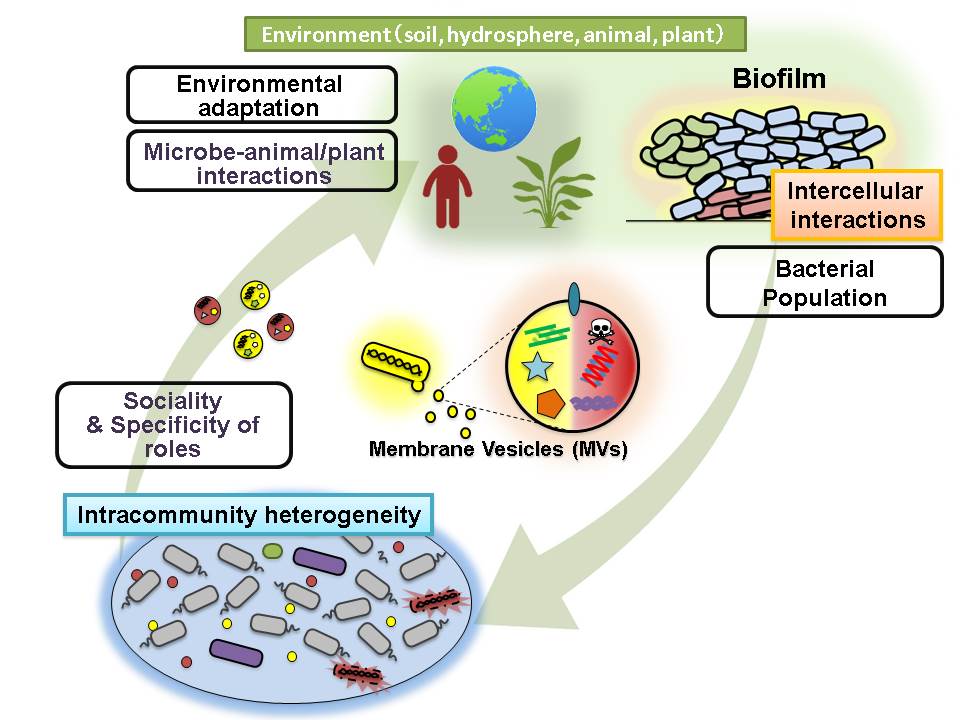
- Microbial ecology studies the relationships between microorganisms and their environments.
- It explores how microorganisms interact with each other and with plants, animals, and other organisms.
- Microbes play vital roles in nutrient cycling, carbon fixation, and maintaining ecosystem balance.
- Microbial communities can be found in various habitats, such as soil, oceans, and human gut.
- Understanding microbial ecology helps in environmental conservation and biotechnological applications.
Interesting fact: Microbes in the ocean produce about half of the world's oxygen through photosynthesis.
- Food microbiology focuses on microorganisms in relation to food production, safety, and preservation.
- It examines the presence of pathogens, spoilage organisms, and beneficial microbes in food.
- Microbes are involved in various food processes, including fermentation and production of dairy products.
- Understanding food microbiology helps ensure food safety and develop methods for food preservation.
- Probiotics, which are beneficial microbes, are commonly used in food products for health benefits.
Interesting fact: Some types of cheese, like blue cheese, are produced through the action of specific molds.
- Virology is the branch of microbiology that focuses on the study of viruses.
- It examines virus structure, classification, replication, and interactions with host cells.
- Viruses cause a wide range of diseases in humans, animals, and plants.
- Virologists work on developing antiviral drugs, vaccines, and diagnostic methods.
- Understanding virology is crucial for preventing and managing viral outbreaks.
Interesting fact: The largest known virus is the Mimivirus, which has a size comparable to some bacteria.
- Medical microbiology focuses on microorganisms that cause diseases in humans.
- It involves the study of pathogenic bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites.
- Microbiologists in this field work on diagnosing and treating infections.
- They also study antimicrobial resistance and develop strategies for infection control.
- Medical microbiology plays a crucial role in public health and clinical medicine.
Interesting fact: The human microbiome, consisting of trillions of microbes, is a hot area of research in medical microbiology.
- Parasitology focuses on the study of parasites, which are organisms that live on or inside other organisms.
- Parasites can be protozoa, helminths (worms), or arthropods.
- They can cause various diseases in humans, animals, and plants.
- Parasitologists study parasite life cycles, transmission methods, and develop strategies for control and prevention.
- Understanding parasitology is essential for managing parasitic infections and their impact on ecosystems.
Interesting fact: Malaria, caused by the Plasmodium parasite, is transmitted through the bite of infected mosquitoes.
- Microbial genetics explores the genetic makeup and variation of microorganisms.
- It involves studying gene expression, genetic transfer mechanisms, and mutation rates.
- Microbial geneticists use tools like DNA sequencing and genetic engineering to understand and manipulate microorganisms.
- Genetic variation in microbes contributes to their adaptability, evolution, and ability to cause diseases.
- Studying microbial genetics provides insights into antibiotic resistance, virulence factors, and microbial evolution.
Interesting fact: The discovery of CRISPR-Cas9 technology revolutionized microbial genetics research and genetic engineering.
- Environmental microbiology focuses on the study of microorganisms in natural environments.
- It explores the roles of microbes in nutrient cycling, bioremediation, and ecosystem processes.
- Environmental microbiologists study microbial communities in soil, water, air, and extreme environments.
- They investigate the impacts of environmental factors on microbial diversity, activity, and function.
- Understanding environmental microbiology contributes to environmental conservation and sustainable practices.
Interesting fact: Microbes in soil play a vital role in breaking down organic matter and releasing nutrients for plant growth.
- Extremophiles are microorganisms that thrive in extreme environments with extreme temperatures, pH levels, salinity, or pressure.
- They can be found in environments such as hot springs, deep-sea hydrothermal vents, acidic lakes, and polar regions.
- Extremophiles have unique adaptations that allow them to survive and even thrive in these harsh conditions.
- Studying extremophiles provides insights into the limits of life on Earth and the potential for life in other extreme environments.
- Extremophiles have applications in various industries, such as biotechnology and astrobiology.
Interesting fact: Some extremophiles can survive in environments with temperatures exceeding 100 degrees Celsius.
- Microbial art involves using microorganisms to create visual artworks or artistic expressions.
- Artists and scientists collaborate to harness the unique properties of microbes, such as pigments and growth patterns.
- Microbial art can include techniques like agar art, bacterial painting, and bio-luminescent installations.
- It highlights the intersection of art, science, and microbiology, sparking curiosity and promoting scientific awareness.
- Microbial art showcases the beauty and diversity of the microbial world.
Interesting fact: Some artists use bacteria to create living paintings that evolve and change over time.
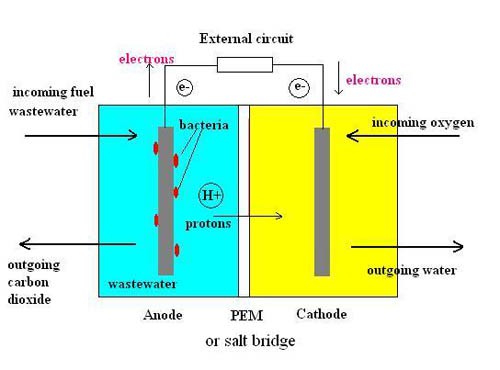
- Microbial fuel cells (MFCs) are devices that generate electricity using the metabolic activity of microorganisms.
- MFCs utilize the electron transfer capabilities of microbes to produce electrical current from organic matter.
- They have potential applications in wastewater treatment, bioenergy production, and remote power sources.
- Research focuses on improving MFC efficiency, scalability, and exploring new microbial catalysts.
- Microbial fuel cells offer a sustainable and renewable approach to power generation.
Interesting fact: Some MFCs can harness electricity from microorganisms naturally present in soil and sediments.
- The microbiome refers to the collection of microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and other microbes, that live in and on the human body.
- These microbes play a crucial role in various aspects of human health, including digestion, immunity, and metabolism.
- The composition and diversity of the microbiome can influence the development of diseases and overall well-being.
- Research on the human microbiome has led to insights into personalized medicine and the potential for microbiome-based therapies.
- Exploring the microbiome opens up new avenues for understanding the complex interactions between microorganisms and their human hosts.
Interesting fact: The total number of microbial cells in the human body is estimated to be ten times greater than the number of human cells.
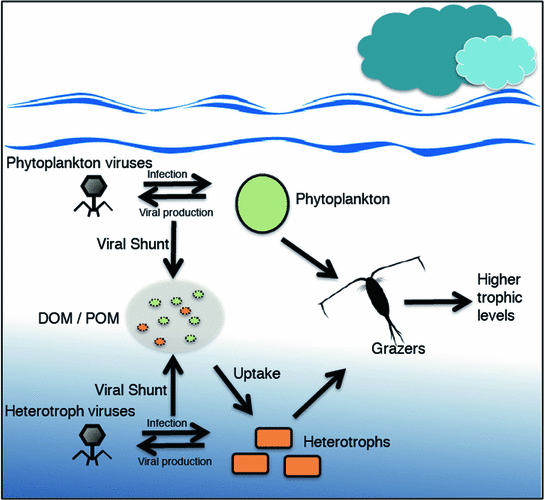
- Viral ecology focuses on studying the ecological interactions between viruses and their environments, including host organisms and ecosystems.
- Viruses play essential roles in various ecological processes, such as nutrient cycling, genetic exchange, and population dynamics.
- Research in viral ecology investigates the diversity, distribution, and impact of viruses in different ecosystems, from oceans to soil to the human body.
- Understanding viral ecology is crucial for comprehending the dynamics of microbial communities and their ecological functions.
- Viral ecology contributes to broader fields like environmental science, evolution, and infectious disease research.
Interesting fact: Viruses are the most abundant biological entities on Earth.
- Archaea are a group of microorganisms that were once classified as bacteria but are now recognized as a distinct domain of life.
- They are found in diverse environments, including extreme habitats such as hot springs, deep-sea hydrothermal vents, and salt lakes.
- Archaea have unique metabolic pathways and adaptations that allow them to thrive in extreme conditions, such as high temperatures, acidity, or salinity.
- They play crucial roles in biogeochemical cycles and have contributed to shaping Earth's ecosystems throughout history.
- Studying archaea provides insights into the origins of life, the evolution of cellular processes, and the limits of life on our planet.
Interesting fact: Some archaea can survive in environments with temperatures exceeding 100 degrees Celsius.
- Phage therapy is an alternative therapeutic approach that uses bacteriophages (viruses that infect bacteria) to treat bacterial infections.
- Each bacteriophage is specific to certain bacterial strains, making them highly targeted and potentially effective against antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
- Phage therapy has a long history and was widely used before the discovery of antibiotics.
- Recent advancements in phage research have renewed interest in this field as a potential solution to combat antibiotic resistance.
- Ongoing studies and clinical trials are exploring the safety and efficacy of phage therapy for various infectious diseases.
Interesting fact: Phages were discovered independently by two scientists, Frederick Twort and Félix d'Hérelle, in the early 20th century.
















No comments:
Post a Comment